When it comes to developing hard goods, there are often mechanical parts. They need to be designed before prototypes start to be made, and this is what’s covered here in phase 5.2. (Don’t forget that you can see the whole series on developing a new product here).
When it comes to developing hard goods, there are often mechanical parts. They need to be designed before prototypes start to be made, and this is what’s covered here in phase 5.2. (Don’t forget that you can see the whole series on developing a new product here).
Mechanical parts can refer to internal mechanisms to drive trains and cases, and everything in between. In other words, all the components of a product that have a physical presence and are not part of the electronics design.
The design is generally carried out using computer-aided design (CAD) software that allows individual physical components to be designed and developed in a three-dimensional space. As individual components are developed, they can be built into an assembly using the same 3D CAD software.
Some of the advantages of using 3D CAD software to design and develop products are:
- Short product design time
- More effective communication with suppliers — factories in China are used to 3D designs
- Visualization of parts and assemblies
- Change from solid to transparent to wireframe, for review and analysis purposes
- Quick and easy to change the design
- Automatic Bill of Materials generation
- Part parameters can be added to calculate weight and part costs
- Part error detection and assembly clash analysis
- Standard part library for ease of adding screws, nuts, bearings and other standard hardware
- 3D data files can be used directly to make products, both prototypes and production
- Data can be emailed to suppliers and customers with ease
- Implementation of a data management process
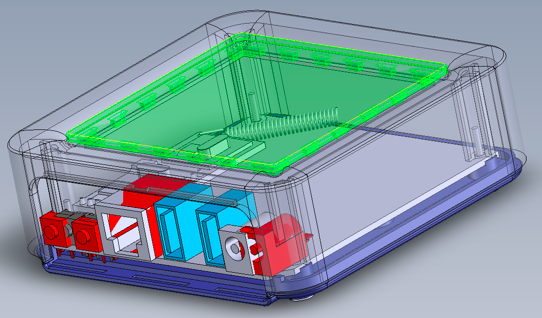
The image above is a screenshot of a product designed using 3D CAD software. In this view, you can see the green top section has been made transparent thus allowing the viewer to see inside the design. The red sections indicate problems from a clash point of view within the assembly itself.
These issues can be fixed before data is released to a supplier who would produce prototype parts. Without the 3D CAD, drawings may have been sent to the supplier, prototype parts made and only when the assembly was put together the clash issues would have been found. This would result in rework and additional parts being made for checking again.
Go to part 8: The Importance of Prototype Build before Production
Want to learn more about the new product introduction process for hardware startups?
In this guide, we explore everything that inventors, SMEs, and hardware startups need to know about making a new product in China and bringing it to market.
We include:
- Why preparation between product design and launch is necessary
- Exploring the NPI process, from product idea to production
- Finding the right manufacturing partner
- Design reviews & adjustments: DFM, DTC, DFQ
- Optimizations for improving cost and quality
- Small production runs before mass production
- Your role in the NPI process