Four types of quality inspection services are usually distinguished. Each one corresponds to a particular step in the production process. They are all part of the toolbox of every importer when it comes to buying in China and other low-cost Asian countries.
Watch the video slideshow of this blog post here
If you like, you can also download the slides for yourself, too.
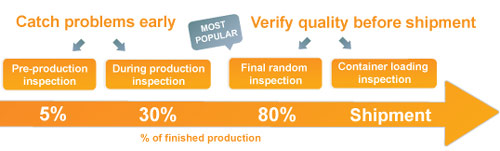
The four types of quality inspection services
I tried to summarize the options available to buyers, in a visual manner.
All quality inspection services are not adapted to the same situation:
Pre-production Inspection
1. A pre-production inspection tells the buyer which kind of raw materials (or components) will be used. Factories are often suspected of lowering their costs by purchasing substandard materials, and this can be disastrous for the buyer (e.g. the wrong kind of chip in an electronic device).
The pre-production inspection can also focus on the processes followed as production starts. Sometimes this can also be critical, as Chinese factories very often cut corners and do not respect the buyer’s blueprints (e.g. patterns for cutting fabric are received from the buyer, and they are modified to make the process easier and faster).
During production inspection
2. A during production inspection (often called “DUPRO” in the industry) allows the buyer to have an idea of average product quality, early in the production cycle. It is the most useful and the most under-rated tool at the disposal of importers, who often only rely on final inspections.
It usually takes place once some finished products have come out of the lines. If quality issues are found, what is already produced might be re-workable, and corrective actions can be taken for the rest of the job. It gives buyers the time to plan ahead, and even to avoid delays (repairs and re-inspections take much more time when problems are noticed after all production is finished).
Watch this video and learn how to improve management of quality from Chinese & Asian suppliers
Final random inspection
3. The final random inspection (also called “pre-shipment inspection”) is by far the most common type of QC check. It takes place once 100% of shipment quantity is finished and at least 80% is packed, so it can be a real random inspection (this is not exactly the case if the quality is checked earlier) and suppliers cannot play games.
It puts pressure on suppliers and gives power to buyers. Its objective is really to confirm a shipment’s quality, rather than catching issues early. Therefore I usually advise my clients to complement final inspections with a DUPRO, to avoid finding disasters at the last minute.
Container loading inspection
4. The container loading inspection, like the pre-production inspection, it is seldom used. But it can be a worthwhile option in some specific cases.
It can be useful if the buyer has a precise loading plan and needs it to be respected very precisely (e.g. some cartons are too fragile to be placed at the bottom), or if the packaging is not conventional (e.g. some garments hung on bars, with no carton protection).
It can also ensure that the right kind of products are shipped out in the right quantity, when the importer places no trust in his supplier or when several suppliers bring their products for consolidation.
Only the most sensitive projects require all four types of inspection. Generally, only one or two of these tools are used, depending on the risks identified by the buyer.
These quality inspection services are used mostly for consumer goods involving little customization. Different approaches are often chosen for ensuring that industrial products are up to specs (much more attention is spent during development and early production).
—
Related posts:
- What is the “AQL” (Acceptance Quality Limit) in simple terms?
- How much does a quality inspection in China cost?
- Checklist for better quality inspections
- Quality Control basic concepts
Sofeast: Quality Assurance In China Or Vietnam For Beginners [eBook]
This free eBook shows importers who are new to outsourcing production to China or Vietnam the five key foundations of a proven Quality Assurance strategy, and also shows you some common traps that importers fall into and how to avoid or overcome them in order to get the best possible production results.
Ready to get your copy? Hit the button below:





15 Responses
Great article, Renaud!
In manufacturing jewelry and textiles in China, we have used all 4 of these practices at one point or another. You covered the bases well and your diagram was descriptive of the process.
Like you, I think the more you prepare beforehand the better the outcome (most likely) will be. “Catching problems early” is the best route to go!
thanks you verey much
Thanks Jill!
How should summarize any final inspection Report. if had been done on Aql level 2.5..
Praveen, I don’t understand…
ya… great article…
Thanks!
very useful details.thank u.
very informative and helpful. thank u so much!
I like their ideas but some problems created infront of me . So kindly all comments give in hindi fonts
Tomorrow exam so I need tonic
Thank you
i don’t have any idea being a quality inspector.but when i go to this site at least it help me find out ..that my job is interesting being a highschool graduete
sir, i place the order paid 50 % payment for the lab equipment, requesting inspection agent send the correct details , my mail nira@bbi.co.bw
Sure. Let us send you an email.
I,M QUALITY INSPECTOR ALSO TNX FOR THIS GUIDE