Ensuring product quality over time is one of the major challenges of all importers. But what makes for an effective quality assurance strategy in China?
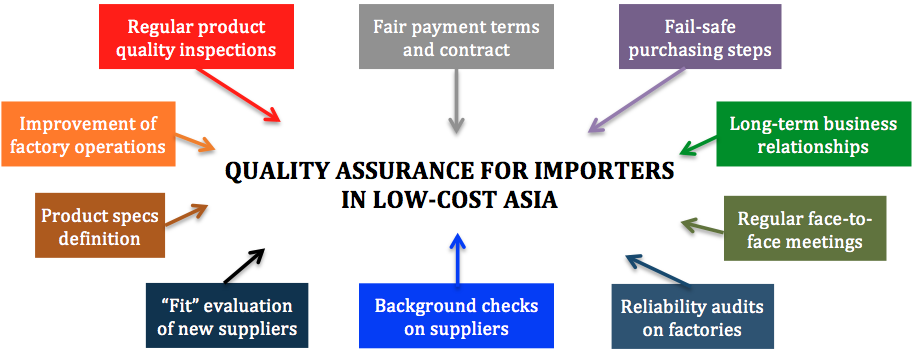
Boiled down to its simplest form, such a strategy contains 10 distinct components:
Note: this QA strategy is not for every importer. It is appropriate for hands-on buyers that know the products they are buying and that must guarantee a certain quality level. The buyers of tens/hundreds of product categories cannot go that deep into each supplier relationship.
I organized the QA strategy’s 10 components into 4 themes:
Theme 1: qualification of new suppliers

1. Background checks on suppliers
Don’t let trading companies pretend that they own a factory. If you want to work directly with a manufacturer, run a background check on the companies that want to work with you. For example, there are many companies that can perform a ‘supplier legal records check’ for you.
Don’t forget to get precise information about the factory where they intend to make your products. And get their written promise that they will not place production anywhere else without your written authorization (it should be included in your contract with the supplier).
2. Reliability audits on factories
Do you want to place orders in a factory that you don’t know? If you can evaluate its capacity and its quality system, go and visit it. If you can’t, appoint a QA/QC agency to do an ISO 9000 audit. Ask for an example of a report before you book the service, to make sure you get what you need.
3. “Fit” evaluation of new suppliers
Factory audits tend to give a higher score to larger manufacturers, simply because they have more organization layers and more written procedures.
However, for your small orders, you might be better served by small factories. In this case, a visit from your staff is necessary. You will evaluate the owner’s personal motivation to take your order and to keep an eye on it every single day. When necessary, don’t hesitate to work with a trading company.
Theme 2: purchasing method
4. Fair payment terms and contract
Once you have paid 100%, you have no more leverage. Don’t think Chinese suppliers are motivated by your next orders. Most of them aren’t.
Try to pay by letter of credit, or limit your deposit to 30%. And do not wire the remainder before shipment (or, in any case, before quality was confirmed by a final inspection).
For your large orders, use an OEM agreement drafted by a lawyer specializing in Chinese law. The key is to be very detail oriented, to pre-define the amount of each penalty, and to ensure that the contract is enforceable in a Chinese court of law.
5. Fail-safe purchasing steps
How do you make sure your purchasers follow the right buying procedure? For example, they should not forget any step in qualifying new suppliers or regarding payments.
You need to set up a buying procedure that incorporates all the QA steps and make sure it is respected by everyone in your company.
Theme 3: quality control
6. Product specs definition
Before issuing an order, your quality department or your QA service provider should define very precisely what you expect to receive. Describe the product and its performance/resistance requirements, but also the packaging and the labeling. Whenever applicable, set limits and tolerances.
Get the supplier to accept the spec sheets (after discussions and revisions if necessary). And make them a part of the contract.
7. Regular product quality inspections
For new manufacturers of new products, make sure you check the quality during production, and again before shipment.
For re-orders, final (pre-shipment) quality control is usually enough. And, for your best suppliers, you might not need to check every shipment.
Theme 4: buyer-supplier relationship
8. Long-term business relationships
Some importers want to “partner” with one factory, by trading regular orders against low pricing and good quality. But it doesn’t work.
What is effective, though, is to make promises and to keep them. And to stay with the same supplier as long as the relationship is good, rather than abandoning them to save a few pennies somewhere else.
When a supplier disappoints you, don’t hesitate to “punish” them by skipping them for one season. Then come back to them slowly.
9. Regular face-to-face meetings
In China, business isn’t done through emails and phone calls. It gets done mostly face to face. Make sure your suppliers know you. Meet their salespeople, but also their managers. You will know who you should call when you run into trouble.
10. Improvement of factory operations
Chinese factory owners can be quite stubborn. However, when their major customer pushes them to improve and sends them warning letters, they listen.
If you have worked with a good supplier for years and if they listen to you, why don’t you pay an engineering firm to improve their processes and their organization? Within a few weeks of work, their labor productivity can certainly be increased by 20%, their cycle time reduced by 30%, and their defects reduced by half. Isn’t it worth an investment from your side?
Get help to handle quality with a tailored Quality Assurance program
If you are developing and manufacturing new products and want to set up a reliable supply chain, implementing a QA program makes a lot of sense. We can help you do this at my company Sofeast. Take a look at what a QA program is and get a quote if you like.
Quality Assurance Policy For Importers In China [Webinar]
What is the 80/20 rule when it comes to QC in China? The answer is building a strong quality assurance policy of your own.
In this webinar, we’re going to explore key challenges facing importers from China, and the elements that compose a really solid, effective quality assurance policy.
Improving your quality assurance will help avoid poor quality products from hurting your business. Hit the button below to register to watch the webinar!


Very good post. This is the way to go. And you know my opinion: buyers who do not want to be hands on should probably stay away from China.
Thanks Etienne. I also agree with you!